
Ronald R. Cherry
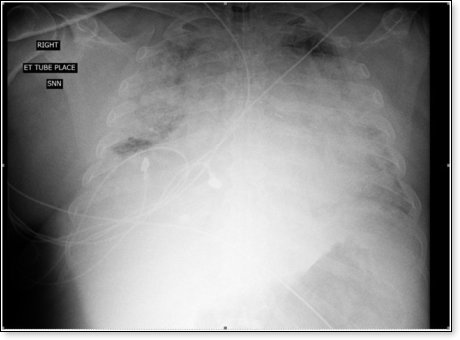
I present here the case report of my 65 year old patient who suffered from critical COVID-19 illness, with profound bilateral pneumonia (ARDS) and severe respiratory failure, requiring intubation and over two weeks of mechanical ventilation. Comorbidities include obesity, hypertension, hyperlipidemia, non-insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus and rheumatoid arthritis. We were discouraged with the lack of improvement despite treatment with IV fluids, enteral nutrition, anticoagulation, corticosteroids, antibiotics, Remdesivir, Ivermectin, convalescent plasma, and the usual level of ICU care. Developing cytokine storm, the patient’s respiratory status progressively deteriorated over several days despite our best efforts, to the point where we believed the patient would die before the next day. Out of desperation, despite warnings from the FDA, we added Hydroxychloroquine and Zinc gluconate to the treatment regimen. With no additional changes the patient’s critical pulmonary illness greatly improved in less than 24 hours. This is the patient’s chest x-ray on the day we added Hydroxychloroquine and Zinc:
This is the chest x-ray the following day:
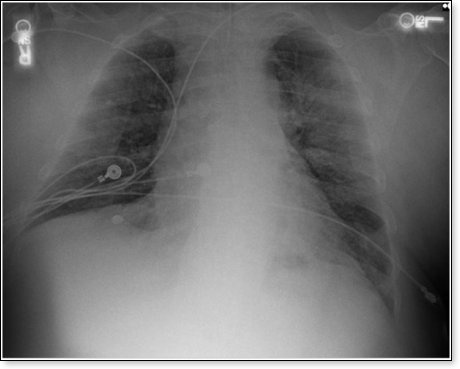
The patient later received a dose of Tocilizumab, further improving the chest x-ray, ARDS, and respiratory failure, and normalization of the CRP (an indicator of inflammation). This patient was subsequently extubated and removed from mechanical ventilation, making a full recovery.
This is only a single case report, but we are having similar success with other hospitalized patients suffering from serious or critical COVID-19 illness with bilateral pneumonia, using the following treatment regimen in addition to usual critical care measures:
- Supplemental oxygen
- BiPap or CPAP as required
- Mechanical ventilation as required. We have observed that pressure-controlled, bi-level, 3:1 inverse-ration ventilation (PCIRV), usually with a respiratory rate of 26-30, is often superior to traditional SIMV ventilation with PEEP
- Full anticoagulation with low molecular weight heparin (usually Lovenox)
- Corticosteroid therapy, either Decadron 4 mg IV bid or Solu-Medrol 40 mg iv bid
- Antibiotic therapy
- Remdesivir 200 mg IV day 1, followed by 100 mg IV for an additional 4 days
- Hydroxychloroquine 400 mg po or per nasogastric tube initially, again after 12 hours, then daily
- Zinc gluconate 50 mg po or per nasogastric tube bid
- Ivermectin 6 mg po or per nasogastric tube, and again after 6 hours, 12 mg total
- Convalescent plasma, 2 units
- Add Tocilizumab 800 mg IV as a single dose for the sickest patients with bilateral pneumonia and overt or impending respiratory failure, requiring BiPap, CPAP or mechanical ventilation
We are not professional medical researchers at my small community hospital in Tennessee, but rather professional medical practitioners, trying our best to save human life during this stressful COVID-19 pandemic. As it is said, we are fighting this terrible disease in the trenches. I hope this case report will prompt professional medical researchers to study the proposed treatment regimen, hoping that it will save many lives.

This case report is made with written permission from the patient, stipulating that no identifying information is contained in the text or in the chest x-ray images.
Ronald R. Cherry, MDBoard Certified in Internal Medicine, Sleep Medicine & Pulmonary Disease
© Ronald R. CherryThe views expressed by RenewAmerica columnists are their own and do not necessarily reflect the position of RenewAmerica or its affiliates.

















